What are tonsils?
The tonsils
have the structure of some glands and are located in the back of the neck, on
the one hand and the other. These are composed of a tissue that contains
lymphocytes - cells that prevent and combat the onset of infections. Tonsils
are believed to play a role in the immune system and are designed to retain
viral particles and bacteria that enter the body through the throat.
However,
most experts say that tonsils often do not work well, becoming an obstacle
rather than a help. Evidence also suggests that people in whom tonsils have
been removed are more likely to suffer from bacterial or viral infections than
those with intact tonsils.
What are the causes of stones formation on tonsils?
The tonsils have
some small pockets in which bacteria and other materials (including dead cells
and mucositis) can be captured. Over time, the accumulated (caseeum) formations
can become concentrated.
Tonsils stones
are formed when these debris is hardened or calcified. The process occurs more
often in people who suffer from chronic tonsil inflammation or recurrent
tonsillitis.
What are the
specific symptoms of tonsillitis?
Several small
stones of the tonsils do not cause any visible symptoms. Even when they are
large, some are accidentally discovered following radiographs or computer
tomography investigations. However, in the case of large tonsils, multiple
symptoms may occur:
- Bad breath
- One of the first signs of amgdalitis is bad smell or halitosis that
accompanies tonsillitis. After a study, subjects with chronic tonsillitis were
analyzed and 75% of people with high concentrations of volatile sulfur in
breathing were those who had stones (caseum) on the tonsils.
- Sore
throat - When sore throats are present with a stone and tonsil infection, it is
hard to tell the cause. The presence of a stones on the tonsils itself can
cause pain or discomfort in the area where it is deposited.
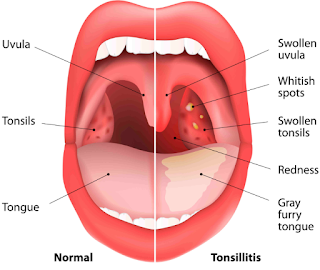
- Whitish
deposits - Some stones on the tonsils may be visible in part from the back of
the neck like a piece of solid white material. However, this is not a rule, as
most are hidden in the crypt of the tonsils. In this case, they can only be
detected using non-invasive scanning techniques (CT or magnetic resonance
imaging).
- Difficulty
swallowing - depending on the location or size of stones on the tonsils,
swallowing food or liquids may become painful.
- Ear pain -
stones on the tonsils can develop anywhere on the tonsils. Because of common
nerve pathways, they can cause pain even at the ear, even if the stone itself
does not touch the ear.
- Swelling -
when the collected remains strengthen and form a stone on the tonsils, the
inflammation produced by the infection (if it exists) and the tonsillitis
itself causes swelling or enlargement of the tonsils.
How do tonsils stones develop?
Tonsils Stones
are still a mystery for doctors and researchers, but it is suspected that those
who have frequently suffered from tonsillitis have an increased risk of
developing stones on their tonsils. This is due to the fact that frequent
infections of the tonsils cause the appearance of excess fibrous tissue. This
can lead to the development of crypts and ribbons from the tonsils.
Dead skin
cells, bacteria, and other substances can be collected within these spaces,
forming a mass of deposits. Salts in saliva can lead to the petrification of
this mass, forming amygdalites. The stones on the tonsils will increase as more
and more food or other remains are accumulated and deposited.
Diagnosing, removing and preventing tonsils stones
The doctor
can diagnose this by examining the neck and can remove the stone manually. In
some cases, radiography or computer tomography may be required to confirm the
diagnosis and to better visualize stones from the tonsils.
If the
tonsillitis does not cause any symptoms or manifestation, treatment will not be
necessary. But if the stone on the tonsils is very large or associated with
worrying symptoms (pain, inflamed tonsils or swallowing problems), treatment
may be necessary. Stones on tonsils are sometimes surgically removed or if it
is large, tonsillioma may be needed.
When you notice
small tonsil stones you can remove them with natural remedies.
Here is how
to remove and prevent tonsil stones naturally at home:
- - Apple
cider vinegar Diluted with water and gargle.
- - Garlic
has antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral properties. It can fight bacterial
growth and infection.
- - Essential
oils: oregano, myrrh,
thieves oil, and lemongrass. These oils have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial
properties and are able to help reduce or eliminate your tonsil stones. Dilute
the essential oil in a carrier oil or honey and place one or two drops on a
toothbrush before brushing the stones.
- - Yogurt
contains probiotics that are able to counteract the bacteria that causes tonsil
stones.
- - Onions
contain strong antibacterial properties that prevent and eliminate tonsil
stones.
The best way
to prevent tonsils stones naturally at home is to avoid the formation of trenches and crypts
from the tonsils by preventing current episodes of tonsillitis. This can be
done by:
- Frequently
washing your hands
- Do not
change tableware, utensils, toothbrush or kiss people suffering from tonsillitis
- informing
your doctor if the episodes of tonsillitis occur frequently (in this case a
tonsillectomy may be necessary).
Also you can check out these fast, safe and completely PAIN-FREE ways to remove tonsil stones from the comfort of your own home HERE.

Comments
Post a Comment